<
Simulation of how a light pulse while traveling through a fiber optics cable
Download Now
Pulse Distortion
This is a simulation that you can download and run on your Windows computer.
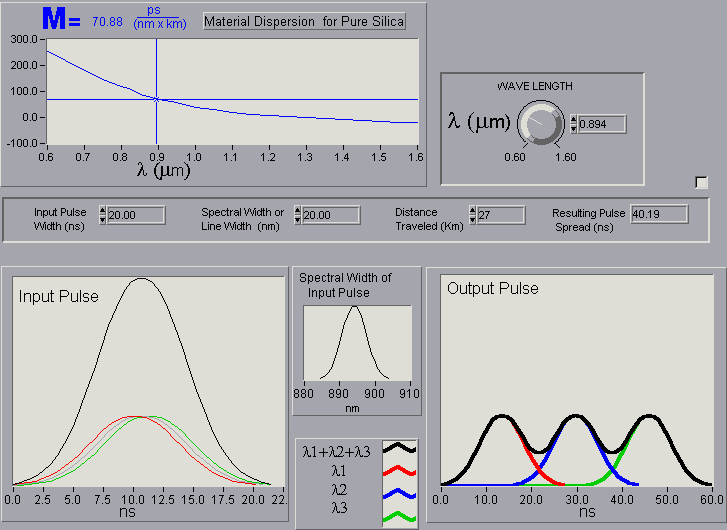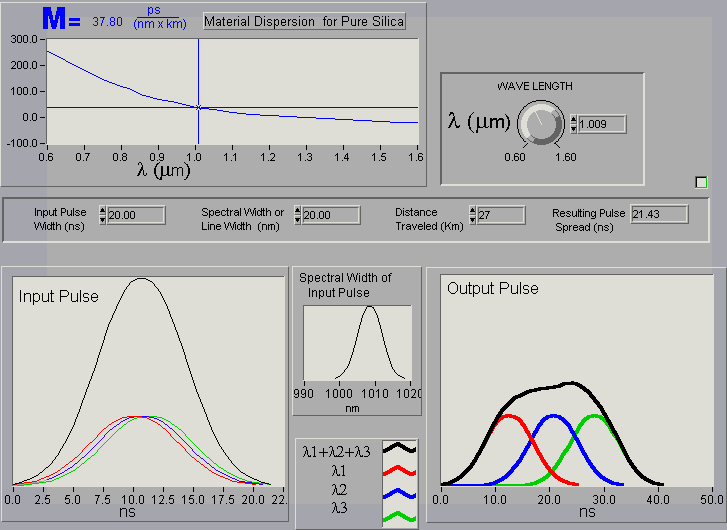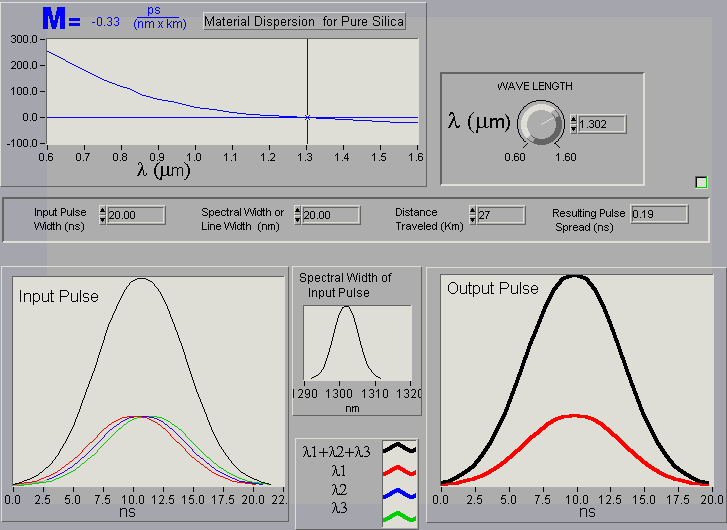
It allows you to see how a pulse becomes distorted while traveling through a medium. In this case the medium is pure silica. To better see what is going on , the input pulse has been broken down into three smaller pulses, each of different wavelength. (The sum of the three pulses equals the large pulse.)
You can adjust the following inputs to see how the pulse is affected:
Wavelength: As you adjust the wavelength, the material dispersion or "M" varies. It is up to you to find the wavelength for which there is the least material dispersion.
Nano Second Pulse Width: This is the time width of your input pulse.
Spectral Width (Line Width): This is the range of wavelength over which your source produces a pulse. The typical spectral width for a light emitting diode can range from 20 to 100 nm. This value is usually determined at the half power points of the pulse. Pulses of different wavelength travel at different speeds. It is up to you to determine if it is best to have a small spectral width or a large spectral width.
Distance Traveled: How far the pulse travels before it reaches the detector.